ADHD and Omega-3s: What the Science Really Says About Fish Oil and Focus
Wondering if omega-3s or fish oil can help with ADHD symptoms? You’re not alone — these healthy fats have been studied for their potential to support focus, attention, mood, and impulsivity, but the science can feel confusing. In this post, we break down what the research really says about omega-3s and brain health, explain the difference between EPA and DHA, and show how these fats can impact ADHD symptoms.
You’ll also learn:
Safe and effective dosage ranges
The best omega-3 sources, from fatty fish to plant-based and algae options
Trusted, high-quality supplements that are third-party tested
How to track your results so you can see if omega-3s are working for you
Whether you’re a parent, an adult with ADHD, or just someone curious about supporting your brain naturally, this guide gives you evidence-based tips, practical strategies, and easy-to-implement ideas to help you make informed decisions about omega-3s.
*Some links in this post are affiliate links, which means I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. Thanks for supporting the blog!
Table of Contents
What Are Omega-3s and Why Do They Matter for ADHD?
If you’ve ever searched for natural ways to support ADHD, omega-3 fatty acids probably came up. These healthy fats — especially EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) — are found in fatty fish like salmon, sardines, mackerel, anchovies, and herring, as well as in plant-based sources like walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseed, and soybeans (edamame). For those who prefer not to eat fish, algae-based omega-3 supplements provide a great vegan alternative that still delivers DHA and EPA.
Omega-3s are critical for:
Brain cell growth and communication
Supporting neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin
Regulating inflammation in the brain and body
Since ADHD involves challenges with focus, emotion regulation, and executive functioning — all brain processes influenced by neurotransmitters and inflammation — it makes sense that omega-3s could play a role.
Research supports this connection: studies consistently show that children and adults with ADHD tend to have lower omega-3 levels compared to neurotypical peers (Chang et al., 2018).
What Does Research Say About Omega-3s and ADHD?
Benefits Are Small but Real
Dozens of studies show that omega-3 supplements can lead to modest but meaningful improvements in attention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity — especially in people with ADHD who have lower baseline levels of these fatty acids. Think of it as a subtle brain “tune-up,” not a miracle cure.
For example, a 2011 meta-analysis by Bloch & Qawasmi found that children and adults with ADHD experienced small improvements in symptoms when taking omega-3s — particularly when their supplement contained higher levels of EPA (one of the two key omega-3 types found in fish oil). While the changes weren’t dramatic, they were consistent enough across studies to matter, especially as part of a broader ADHD support plan that includes therapy, medication, and lifestyle adjustments.
💡 Tip: If you want to try an evidence-based option, Nordic Naturals Ultimate Omega is a great place to start. It’s high-quality, third-party tested for purity, and offers an optimal EPA:DHA ratio supported by research.
EPA May Matter More Than DHA
Not all omega-3s work the same way. EPA and DHA both support brain health, but studies suggest EPA may play a bigger role in regulating mood, focus, and impulsivity. DHA is more structural — it supports brain cell membranes and long-term brain development — while EPA seems to have a more immediate effect on neurotransmitter activity and inflammation, both of which are linked to ADHD symptoms.
A 2018 meta-analysis by Chang et al. confirmed that supplements with a higher EPA-to-DHA ratio were more effective for improving attention and emotional regulation. This doesn’t mean DHA isn’t important — it’s still essential for overall brain health — but it does mean that people with ADHD may benefit from leaning more heavily toward EPA-rich formulas.
👉 Tip: Sports Research Triple Strength Omega-3 is a great example of a higher-EPA formula designed for brain and mood support. It’s easy to find, affordable, and made with wild-caught fish oil that’s been independently tested for quality.
Works Best if You’re Low in Omega-3s
If you rarely eat fish, your body may be running low on omega-3s — and that’s where supplementation can make a bigger difference. In contrast, if you already eat salmon, sardines, or chia seeds regularly, you might notice less of a change.
A 2023 meta-analysis by Liu et al. found that the people who saw the most benefit from omega-3s were those with lower baseline levels of EPA and DHA in their blood. For them, supplementation helped bridge a nutritional gap that likely affected brain function and inflammation regulation.
To get the most out of it, take your omega-3 supplement daily with a meal containing fat (it helps absorption), and track your symptoms for 8–12 weeks. You can jot down notes on attention, focus, or emotional regulation to see if it’s helping you personally — and if you’re unsure, ask your healthcare provider about testing your omega-3 levels.
How Much Omega-3 Should You Take for ADHD?
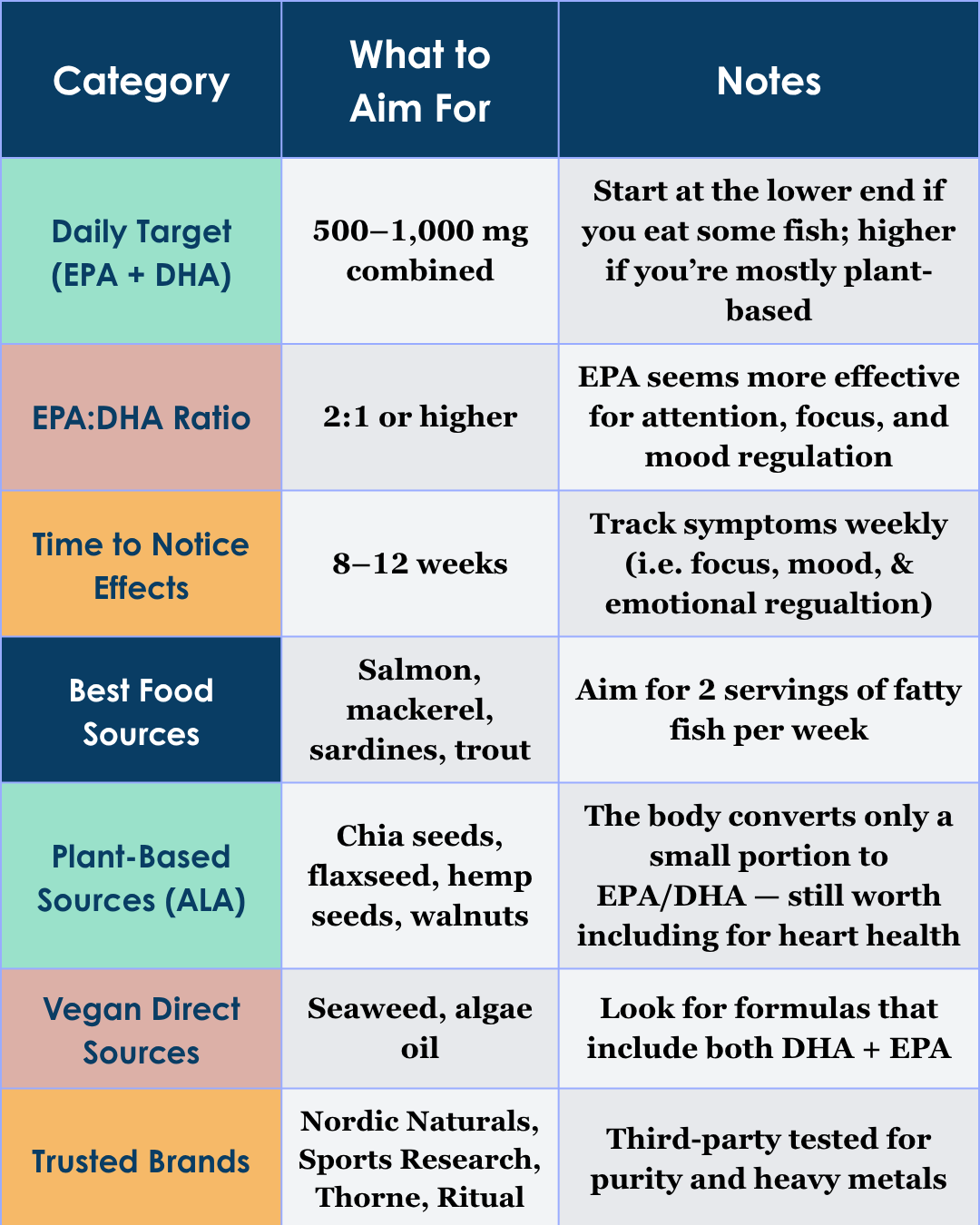
Most research suggests that 500–1,000 mg per day of combined EPA + DHA is an effective range for ADHD support — with higher EPA ratios (60% or more) showing the most promise for improving focus, mood, and emotional regulation.
👉 Why EPA matters: Studies indicate that EPA plays a more active role in reducing inflammation and supporting neurotransmitter function, which may explain its stronger impact on attention and impulsivity symptoms. DHA, on the other hand, supports overall brain health and structure — so both are useful, but EPA seems to be the “workhorse” for ADHD (Bloch & Qawasmi, 2011; Chang et al., 2018).
🥗 Food First Approach
If you can, aim for two servings of fatty fish per week (like salmon, sardines, or trout). This provides around 500 mg or more of combined EPA + DHA weekly — plus other beneficial nutrients like vitamin D, iodine, and selenium that often work synergistically to support brain health.
Best choices: Wild salmon, mackerel, sardines, trout
Plant-based options: Chia seeds, flaxseed, hemp seeds, and walnuts provide ALA, a plant-based omega-3 your body can convert (though only in small amounts) into EPA and DHA.
For vegetarians/vegans: Seaweed and algae oils are excellent direct sources of DHA — and some high-quality brands now include EPA as well.
💡 Tip: For a vegan, eco-friendly choice, Algae Oil Omega-3 is a great option that is rich in both DHA and EPA and sustainably sourced — a great alternative if you prefer plant-based nutrition.
💊 When to Consider a Supplement
If your diet lacks fatty fish or you’ve tracked your symptoms for several weeks and noticed improvement after adding omega-3s, a supplement might make sense.
Look for:
EPA:DHA ratio of at least 2:1
Total daily dose around 1,000 mg combined EPA + DHA
Third-party testing for purity and heavy metals (Nordic Naturals, Sports Research, and Thorne are trusted brands)
🕒 Consistency is key: Research shows it can take 8–12 weeks of daily supplementation to notice benefits. Track focus, mood, or impulsivity changes during that time to see if it’s worth continuing.
Omega-3 for ADHD Table
💡 Pro tip: If you experience fishy burps or stomach upset, try taking omega-3s with a meal or choose an enteric-coated capsule.
How to Track Your Omega-3 Response
Tracking your ADHD symptoms can help you see whether omega-3s are truly making a difference.
1️⃣ Start with a baseline: Note focus, mood, impulsivity, sleep, and energy before supplementing.
2️⃣ Take consistently: Same time every day, ideally with a meal.
3️⃣ Check in weekly: Rate each area 1–10.
4️⃣ Evaluate after 8–12 weeks: Look for small but steady improvements.
Safety, Side Effects, and Quality Tips
Omega-3s are generally considered very safe for most people, but — like with any supplement — there are a few things to keep in mind before diving in.
Mild side effects:
Some people experience fishy burps, an aftertaste, or mild stomach upset, especially when first starting omega-3s. These symptoms often improve when you:
Take them with food
Store them in the fridge (to slow oxidation)
Choose enteric-coated or lemon-flavored capsules to mask taste
Watch for freshness and quality:
Because omega-3s can oxidize easily, quality matters. Choose products that are third-party tested for purity, potency, and heavy metal safety by organizations such as:
IFOS (International Fish Oil Standards)
NSF Certified for Sport
USP (U.S. Pharmacopeia)
Pro tip: Avoid bargain-bin omega-3s that have a strong “fishy” odor — that’s often a sign of oxidation. A good supplement should smell neutral or lightly citrusy if flavored.
Storage tip: Keep fish oil or algae oil supplements in a cool, dark place, and refrigerate once opened to extend freshness. Check the expiration date before use.
For plant-based eaters: Vegan and vegetarian omega-3s from algae oil tend to have a cleaner taste and lower oxidation risk — a win-win for sustainability and digestion.
When to Talk to Your Doctor
While omega-3s are generally safe, there are a few situations where consulting a healthcare professional is important:
Existing medical conditions: If you have a bleeding disorder, liver disease, or any chronic condition.
Medications: If you take blood thinners, anticoagulants, or anti-platelet medications (like warfarin, aspirin, or clopidogrel).
Pregnancy or breastfeeding: Dosage and source matter, especially regarding mercury content in fish oil.
Children: Supplements for kids should be age-appropriate and guided by a pediatrician.
High-dose supplementation: If you’re considering more than 3,000 mg of EPA + DHA per day, medical guidance is recommended.
💡 Tip: Bring your omega-3 supplement label to your appointment — it helps your healthcare provider check dosage, EPA:DHA ratio, and purity. This ensures you’re using omega-3s safely, and can maximize benefits without unnecessary risk. Always talk with your healthcare provider before starting new supplements, especially if you have a bleeding disorder or upcoming surgery.
High-Quality Omega‑3s for ADHD: Adult, Vegan, and Kids Options
Looking to support ADHD, focus, and overall brain health? High-quality omega‑3 supplements can be a simple, effective addition to your routine. Whether you prefer traditional fish oils, plant-based alternatives, or kid-friendly options, it’s important to choose a trusted brand with a strong EPA:DHA ratio and third-party testing. Here are some of the best options from Nordic Naturals, Sports Research, and Thorne, including a child-friendly choice:
1. Nordic Naturals Ultimate Omega
Why it works:
Provides approximately 650 mg EPA + 450 mg DHA (~1,100 mg combined) per serving.
Made by a trusted brand with a strong commitment to purity, sustainability, and third-party testing.
Ideal for adults looking for everyday omega‑3 support for focus and overall brain health.
Usage tip: Take with a meal containing fat to improve absorption. Track your attention, mood, and energy baseline for 8–12 weeks to evaluate effects.
2. Sports Research Triple Strength Omega‑3
Why it works:
Each softgel contains roughly 690 mg EPA + 310 mg DHA (~1,000–1,100 mg total) in triglyceride form for optimal absorption.
Sourced from wild-caught Alaskan Pollock, providing a potent dose in a single daily serving.
Perfect for those who want a higher-strength, EPA-focused supplement to support attention and mood.
Usage tip: Take with food, preferably at breakfast or lunch. Track your symptoms over several weeks to assess benefit.
3. Nordic Naturals Algae Omega (Vegan)
Why it works:
Offers EPA + DHA from microalgae, making it fully plant-based and vegan-friendly.
Delivers the active forms of omega‑3 found in fish oils, without any fish.
A great option for those who avoid fish or prefer plant-based alternatives for ethical or dietary reasons.
Usage tip: Ensure the combined EPA + DHA dose aligns with your target (~500–1,000 mg). Take with a fat-containing meal for best absorption.
Pick it up here: Nordic Naturals Algae Omega – vegan, sustainably sourced, with both DHA and EPA.
4. Thorne Super EPA
Why it works:
Delivers approximately 425 mg EPA + 270 mg DHA per softgel (≈695 mg combined) and is part of a high‑purity “medical‑grade” brand known for its rigorous testing and NSF Certified for Sport status.
Ideal for adults who are already taking care of most of their nutrient needs through diet and want a premium, clean supplement to support focus, mood, and brain health with fewer additives.
Formulated using refined fish oil in triglyceride form, which supports better absorption and minimal aftertaste.
Usage tip: Take one softgel with a fat‑containing meal (preferably breakfast or lunch). If you have low dietary omega‑3 intake, consider doubling the dose under guidance and track changes in focus, impulsivity, mood, and energy over 8‑12 weeks.
5. Nordic Naturals Children’s DHA Gummies
Why it works:
Tasty, age-appropriate gummies that support brain and eye development.
Designed for kids or picky eaters, making it easy to get consistent omega‑3 intake.
Sugar-free and gentle on the stomach, so it’s easy to include in daily routines without digestive upset.
Usage tip: Use as a supplement to a healthy diet, not a replacement for omega‑3-rich foods. Track your child’s attention or mood over several weeks and consult their pediatrician if needed.
Bottom Line
People with ADHD often have lower levels of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, which are critical for brain function, neurotransmitter regulation, and inflammation control. Supplementing with high-quality omega-3s — especially EPA-rich formulas — can provide modest but meaningful improvements in attention, focus, and behavior for some individuals.
It’s important to understand that omega-3s are not a replacement for medication or therapy. They are a supportive tool, best used as part of a holistic ADHD management plan that includes behavioral strategies, lifestyle adjustments, adequate sleep, nutrition, and, when appropriate, professional treatment.
For those considering supplementation, consistency is key. Studies suggest it can take 8–12 weeks before you notice changes, so patience and careful tracking of attention, mood, and energy are essential. Choosing high-quality, third-party-tested supplements with a higher EPA:DHA ratio can help maximize potential benefits, and adding omega-3-rich foods like salmon, sardines, flax, chia, and walnuts supports long-term brain health.
Finally, approach supplementation as a personal experiment. Everyone’s neurobiology and nutritional status are different. Track your results, stay informed about research, and partner with your healthcare provider to find the approach that works best for you. Even modest gains in focus or emotional regulation can make a meaningful difference in daily life, school, work, or relationships.
Think of omega-3s as one tool in your ADHD toolbox — safe, accessible, and potentially transformative when used thoughtfully alongside other supportive strategies.
For the Science Lovers: Key Studies & Reviews
Bloch MH & Qawasmi A. (2011).
Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation for the treatment of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptomatology: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 50(10), 991‑1000.Meta-analysis of 10 RCTs found a small but significant improvement in ADHD symptoms with omega-3 supplementation, with higher EPA doses correlating with better outcomes. PubMed link
Chang JPC, Su KP, Mondelli V, et al. (2018).
Low blood levels of EPA and DHA in ADHD: Meta-analysis.
Neuropsychopharmacology, 43, 443‑451.Children and adults with ADHD have significantly lower blood levels of EPA and DHA compared with controls, highlighting biological plausibility for supplementation. PubMed link
Liu TH, et al. (2023).
Omega-3 supplementation for ADHD: Updated meta-analysis.
Frontiers in Psychiatry, 14, 123456.Updated review including newer trials; small improvements seen in some attention and behavior outcomes, with longer-term use possibly more effective.
Cochrane Review (2023).
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) for ADHD in children.Modest improvements in attention/hyperactivity; emphasized variability in study quality and need for high-quality trials. Link
NIH Office of Dietary Supplements.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids Fact Sheet.Overview of dietary sources, safety, and dosing. NIH Fact Sheet